Software Speeds Up Drug Development
Researchers develop novel method to predict the morphology of sugar coats on clinically relevant proteins within minutes
Sugars cover nearly all proteins present at the surface of the cells in our bodies, forming a shield around the proteins. Thus, these sugars influence how cells interact with their environment including pathogens, playing an important role in medical drug development. GlycoSHIELD, a new computational approach to study the sugar shields of proteins, is resource-reducing, time-efficient and user-friendly. It was developed in the frame of the Max Planck Society's Dioscuri Programme in a Polish-German cooperation project through international collaborations with researchers in France, Taiwan and Germany.
Text: Katharina Kaefer
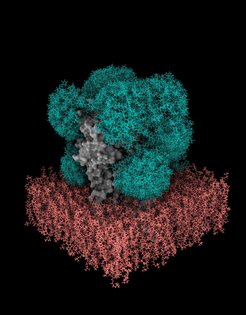
Proteins not only carry out the functions that are critical for the survival of cells, but also influence the development and progression of diseases. To understand their role in health and disease, researchers study the three-dimensional atomic structure of proteins using both experimental and computational methods. Over 75% of proteins present at the surface of our cells are covered by glycans. These sugar-like molecules form very dynamic protective shields around the proteins. However, the mobility and variability of the sugars make it difficult to determine how these shields behave, or how they influence the binding of drug molecules. Mateusz Sikora, the project leader and head of the Dioscuri Centre for Modelling of Posttranslational Modifications, and his team in Krakow and partners at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt am Main, Germany, have addressed this challenge by using computers, working together with scientists at Inserm in Paris, Academia Sinica in Tapei and the University of Bremen. Their powerful new algorithm GlycoSHIELD enables a fast but realistic modeling of the sugar chains present on protein surfaces. Reducing computing hours and therefore power consumption by several orders of magnitude compared to conventional simulation tools, GlycoSHIELD paves the path towards green computing. The scientists published their new method and its validation in the renowned journal Cell.
From thousands of hours to a few minutes
Protective glycan shields strongly influence how proteins interact with other molecules such as therapeutic drugs. For example, the sugar layer on the spike protein of the coronavirus hides the virus from the immune system by making it difficult for natural or vaccine-induced antibodies to recognize the virus. The sugar shields therefore play an important role in drug and vaccine development. Pharmaceutical research could benefit from routinely predicting their morphology and dynamics. Until now, however, forecasting the structure of sugar layers using computer simulations was only possible with expert knowledge on special supercomputers. In many cases, thousands or even millions of computing hours were required. With GlycoSHIELD, Sikora's team provides a fast, environmentally friendly open source alternative. “Our approach reduces resources, computing time and the technical expertise needed,” says Sikora. “Anyone can now calculate the arrangement and dynamics of sugar molecules on proteins on their personal computer within minutes, without the need of expert knowledge and high-performance computers. Furthermore, this new way of making calculations is very energy efficient.” The software can not only be used in research, but could also be helpful for the development of drugs or vaccines, for example in immunotherapy for cancer.
A jigsaw puzzle made of sugar
How did the team manage to achieve such a high increase in efficiency? The authors created and analyzed a library of thousands of most likely 3D poses of the most common forms of sugar chains on proteins found in humans and microorganisms. Using long simulations and experiments, they found that for a reliable prediction of glycan shields, it is sufficient that the attached sugars do not collide with membranes or parts of the protein. The algorithm is based on these findings. “GlyoSHIELD users only have to specify the protein and the locations where the sugars are attached. Our software then puzzles them on the protein surface in the most likely arrangement,” explains Sikora. “We could reproduce the sugar shields of the spike protein accurately: they look exactly as what we see in the experiments!” With GlycoSHIELD it is now possible to supplement new as well as existing protein structures with sugar information. The scientists also used GlycoSHIELD to reveal the pattern of the sugars on the GABAA receptor, an important target for sedatives and anesthetics.
A success for the Dioscuri Centre
The Dioscuri Centres initiated by the Max Planck Society are intended to help strengthen and expand excellent research in Central and Eastern Europe. Since May 2023, Mateusz Sikora, formerly a postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics, has been receiving financial support in the bilaterally funded program as head of the Dioscuri Centre for Modelling of Posttranslational Modifications created at Jagiellonian University in Krakow, Poland. Gerhard Hummer, Head of the Department of Theoretical Biophysics at the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics, supports him as his partner from Germany and also contributed to this work. After less than a year, Sikora has already scored a major success with his green algorithm and is helping to promote Poland as an attractive and competitive research location.
Further information
GlycoSHIELD as web application hosted by the Max Planck Computing and Data Facility:
https://dioscuri-biophysics.pages.mpcdf.de/glycoshield-md/
Information on the Disocuri Programme:
https://www.mpg.de/dioscuri
Websites of the Disocuri Centre for Modelling of Posttranslational Modifications:
https://www.biophys.mpg.de/dioscuri-centre-for-modelling-of-posttranslational-modifications
https://mcb.uj.edu.pl/sikora-lab













